The classification of organisms into distinct categories is crucial for understanding the diversity of life on Earth. Among the major taxonomic groups, birds and mammals occupy prominent positions due to their remarkable adaptability and ecological importance. While it is widely known that birds are avian creatures, some misconceptions and similarities have led to questions regarding their classification as mammals. In this essay, we will delve into the defining characteristics of birds and mammals, comparing and contrasting their anatomical, physiological, and evolutionary traits to clarify their distinct identities.
Understanding Birds
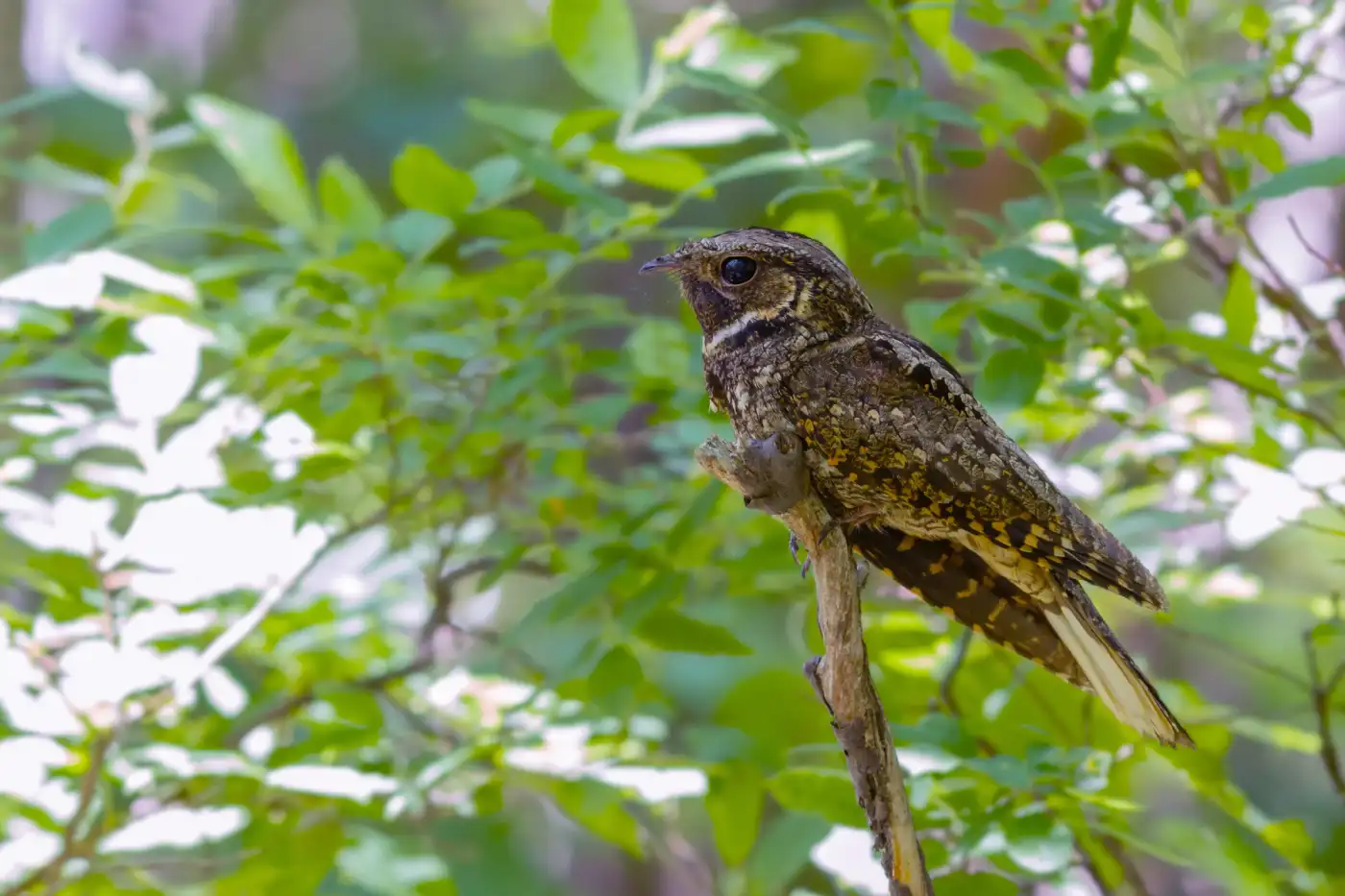
Birds, belonging to the class Aves, are vertebrate animals characterized by various unique features. Feathered wings, beaks, and the ability to fly are some of the key attributes that differentiate them from other organisms.
Birds have adaptations for flight
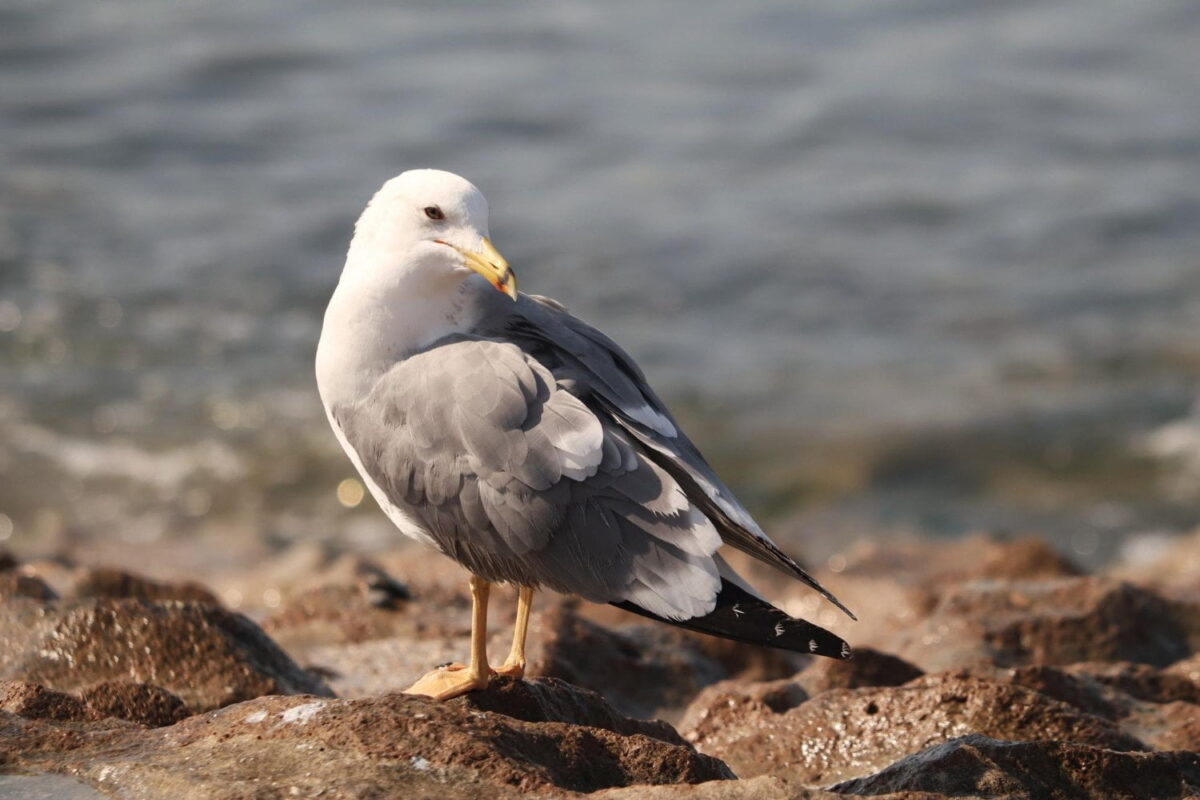

such as lightweight skeletal structures, specialized respiratory systems, and powerful musculature.
Birds are endothermic
meaning they can regulate their body temperature efficiently.
- Birds lay eggs as a mode of reproduction.
- Birds possess a range of beak shapes and sizes that are suited to their respective diets and ecological niches.
- Birds have distinct vocalizations and complex plumage patterns.
- Communication methods of birds vary, and they also use their plumage patterns for mating displays.
Defining Mammals
- Mammals, classified under the class Mammalia, share several defining characteristics. The most notable feature of mammals is their ability to nurse their young with milk produced by mammary glands. The presence of hair or fur on their bodies serves as insulation and protection.
- Mammals possess a specialized set of teeth, including incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, which are adapted to their specific diets. Most mammals give live birth, and their offspring are nourished through the placenta during gestation. Additionally, mammals have a highly developed neocortex, which facilitates complex cognitive abilities and social behaviors.
Comparative Anatomy and Physiology
Examining the anatomical and physiological features of birds and mammals offers further insights into their distinct classifications. While both groups are vertebrates, they display fundamental differences.
- Anatomical and physiological features provide insights into the distinct classifications of birds and mammals.
- Mammals possess a diaphragm, a muscular partition separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities, which birds lack.
- Birds have a unique respiratory system with air sacs, enabling efficient unidirectional airflow during respiration.
- Mammals have a different lung structure that allows for bidirectional airflow.
- Birds have a four-chambered heart similar to mammals, but their hearts are proportionately larger and exhibit adaptations to support the high metabolic demands of flight.
- Mammals possess a specialized ear structure with three middle ear bones (malleus, incus, and stapes).
- Birds, on the other hand, have a single middle ear bone called the columella.
- These differences in anatomy and physiology serve as clear evidence for the distinction between birds and mammals.
Evolutionary Relationships
Understanding the evolutionary history of birds and mammals sheds further light on their distinct identities. Both groups belong to the broader class of amniotes, which includes reptiles, birds, and mammals.
- Birds are descendants of theropod dinosaurs, indicating a shared ancestry with reptiles.
- The evolution of birds is characterized by the development of feathers, the ability to fly, and adaptations for aerial locomotion.
- Mammals also share a common ancestor with reptiles but have diverged to develop unique mammalian characteristics over time.
- The evolutionary paths of birds and mammals showcase their distinct evolutionary trajectories and adaptations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while birds and mammals share certain superficial similarities, a thorough examination of their defining characteristics, anatomy, physiology, and evolutionary history clarifies their distinct classifications. Birds, with their feathers, beaks, ability to fly, and unique respiratory systems, firmly belong to the class Aves. Mammals, characterized by their milk-producing mammary glands, hair or fur, specialized teeth, and complex brain structures, fall under the class Mammalia. Understanding the unique traits and evolutionary paths of birds and mammals helps us appreciate the incredible diversity of life on our planet.